Legionnaires disease special
How to stay safe from Legionnaires
The news from Portland, just off Weymouth, is grim. The water system on board the Bibby Stockholm barge has been found to contain the Legionnaire’s disease bacterium, which causes a type of pneumonia. The government apparently knew about the risk before the barge was evacuated, putting all 39 asylum seekers on board at serious risk. So what is the disease, and how can you protect people against it at your place?
About legionella
The bacterium L. pneumophila was first identified in 1977, when it caused an outbreak of serious pneumonia in a USA convention centre. Since then it has been found in water systems inside buildings around the world. The easiest way to catch it is to breathe in small particles of bacteria via contaminated water sprays, jets, mists, or even ice.
Legionnaire’s symptoms and treatment
There’s antibiotic treatment for legionnaires disease, but no vaccine. Like so many diseases it impacts the vulnerable most of all – and it tends to affect males and those aged over 50 the most. The incubation period is usually 2 to 10 days but can run for as long as 16 days.
Luckily most of the time the illness isn’t serious. But if there’s a delay in diagnosis or treatment or it’s left untreated, it gets steadily worse throughout the first week. If you get a bad dose or you’re vulnerable you can end up with progressive pneumonia with respiratory failure, shock and multi-organ failure – which leads to death.
Poorly maintained water systems are often the cause
Worldwide, waterborne Legionella pneumophila is the most common cause of the disease. It’s widely associated with poorly maintained artificial water systems like the one inside the barge. Nobody knows how much of it you need to breathe in before you get ill, but the infective dose is likely to be pretty low for susceptible people, with only a short exposure time.
The likelihood of illness depends on how much legionella is in the water, the virulence of the strain and the vulnerability of the people it infects. Air conditioning cooling towers, hot and cold water systems, humidifiers and whirlpool spas, breathing in contaminated water or ice are all implicated.
Legionella symptoms and death rate
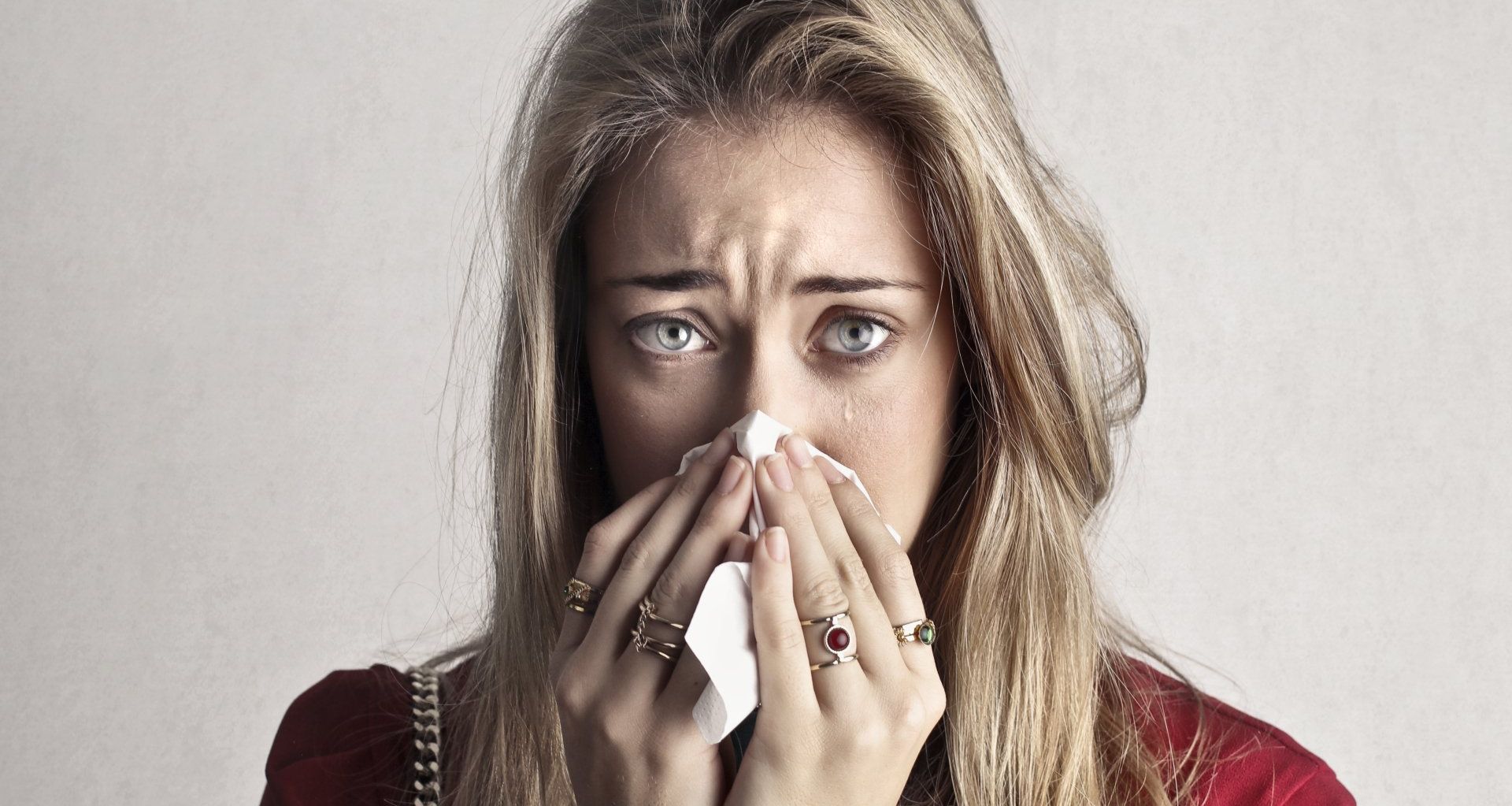
The initial symptoms can include a mild cough or bloody phlegm, fever, loss of appetite, headache, malaise and lethargy, sometimes with muscle pain, diarrhoea and confusion.
The most common complications are respiratory failure, shock, acute kidney failure and multi-organ failure. Recovery depends on antibiotic treatment and can take several weeks or even months.
The death rate can be as high as 40–80% in untreated immuno-suppressed people, but the overall death rate usually falls somewhere between 5–10%.
Our UVC disinfection units kill legionella bacteria
Water safety plans are key to safety. Responsible organisations carry out regular monitoring of control measures set in place against the risk that has been identified, plus good maintenance, regular cleaning and disinfection via high temperature treatments and chemical biocides... or you could keep people safe the simple way using our UVC units.
As revealed by our UVC kill list, our UVC disinfection units kill legionella fast and efficiently. It’s just one of an enormous list of health threats that are made safe by our technology – which is affordable, effective, simple, proven - and really easy and safe to use.